Linux - Samba Setup Rocky 9
Step 1: Install Samba on Linux
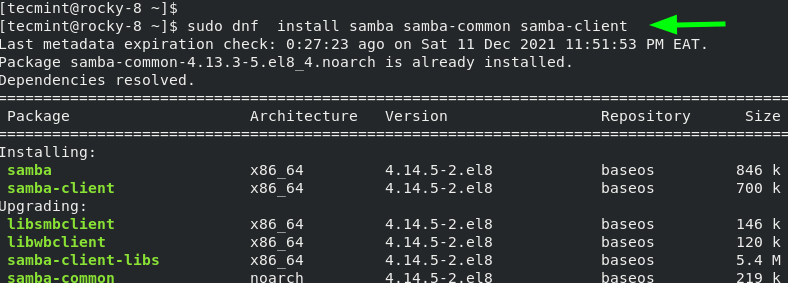
To get started out with Samba, install the Samba core packages including the client package:
dnf install -y samba samba-common samba-client Install-Samba in Linux
The command installs the packages specified along with the dependencies as displayed on the output. After the installation is complete, you will get a summary of all the packages that have been installed.
Samba Installation Completes
Step 2: Create and Configure Samba Shares
Once all the samba packages have been installed, the next step is to configure the samba shares. A samba share is simply a directory that is going to be shared across client systems in the network.
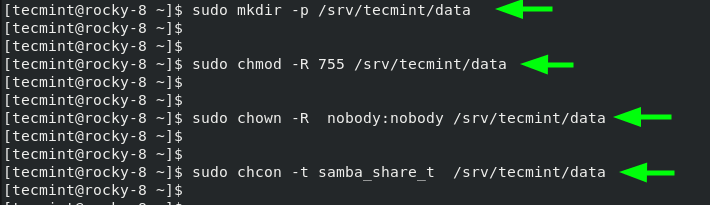
Here, we are going to create a samba share called /data in the /srv/tecmint/ directory path.
mkdir -p /srv/tecmint/dataNext, we will assign permissions and ownership as follows.
chmod -R 755 /srv/tecmint/data
chown -R nobody:nobody /srv/tecmint/data
chcon -t samba_share_t /srv/tecmint/dataNext, we are going to make some configurations in the smb.conf configuration file which is Samba’s main configuration file. But before we do so, we will back up the file by renaming it with a different file extension.
mv /etc/samba/smb.conf /etc/samba/smb.conf.bakNext, we are going to create a new configuration file.
vim /etc/samba/smb.confWe will define policies on who can access the samba share by adding the lines shown in the configuration file.
[global]
workgroup = WORKGROUP
server string = Samba Server %v
netbios name = rocky-8
security = user
map to guest = bad user
dns proxy = no
ntlm auth = true
[Public]
path = /srv/tecmint/data
browsable =yes
writable = yes
guest ok = yes
read only = noSave and exit the configuration file.
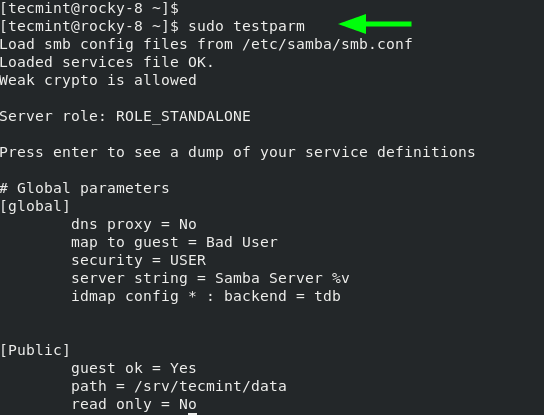
To verify the configurations made, run the command:
testparmVerify Samba Configuration
Next, start and enable Samba daemons as shown.
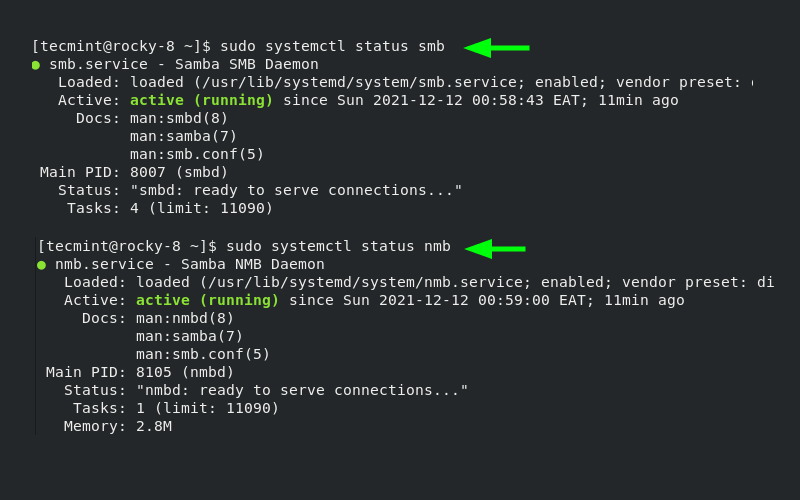
systemctl enable --now smb;systemctl enable --now nmbBe sure to confirm that both the smb and nmb daemons are running.
systemctl status smb;systemctl status nmbVerify Samba Status
To enable access to samba share from remote Windows systems, you need to open the samba protocol on the firewall.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=samba
firewall-cmd --reload
firewall-cmd --list-servicesStep 3: Accessing Samba Share from Windows
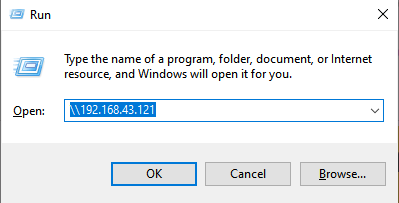
Thus far, we have installed samba and configured our samba share. We are now ready to access it remotely. To do this on a Windows client, press the Windows logo key + R to launch the Run dialog.
In the textfield provided, enter the samba server’s IP address as shown:
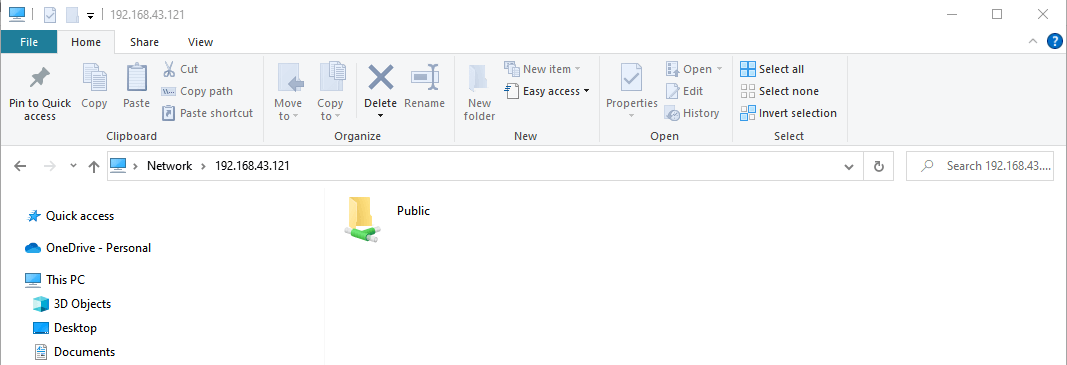
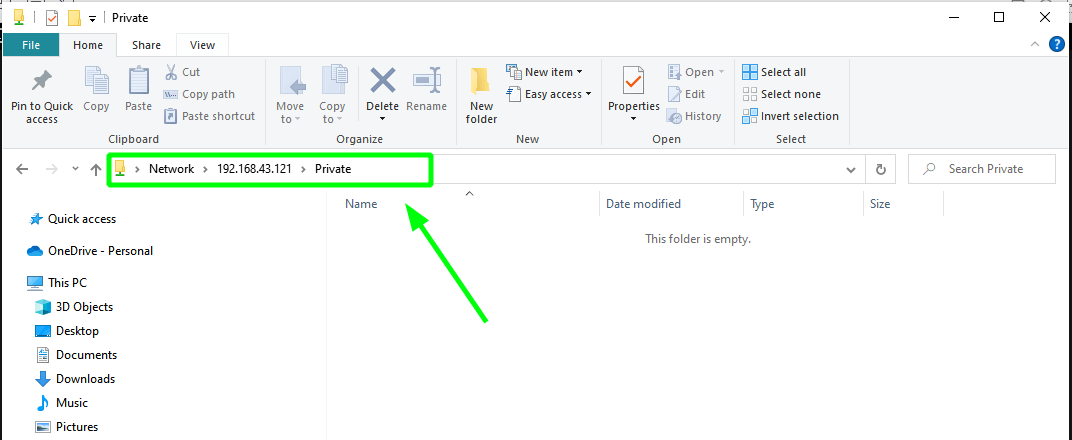
\\server-ipThe following window labeled ‘Public’ will pop up. Remember, this is the directory that points to our samba share in the /srv/tecmint/data directory.
Currently, our directory is empty as we have not created any files. So, we will head back to our terminal and create a few files in the samba share directory.
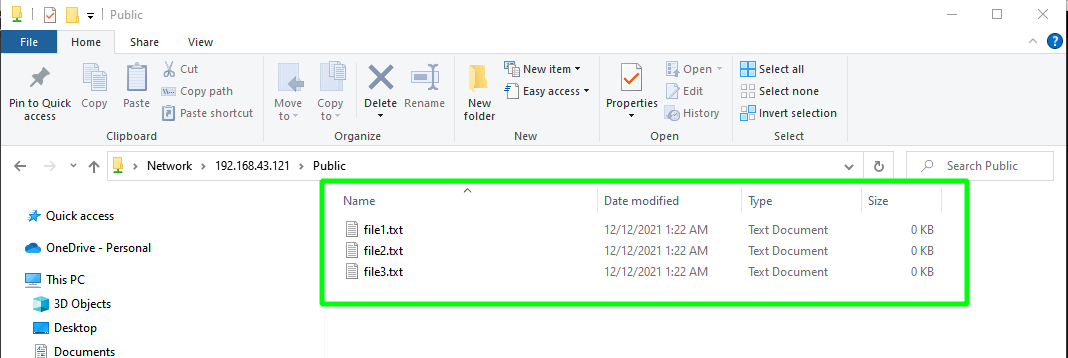
cd /srv/tecmint/data
touch file{1..3}.txtPerfect. We have successfully managed to access our samba share. However, our directory is accessible to anyone and everybody can edit and delete files at will, which is not recommended especially if you plan to host sensitive files.
In the next step, we will demonstrate how you can create and configure a secure samba share directory.
Step 4: Secure Samba Share Directory
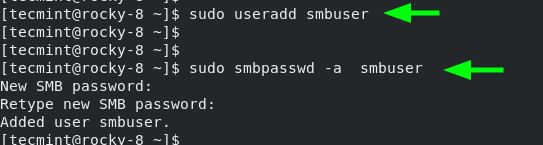
First, we will create a new samba user.
useradd smbuserNext, we will configure a password for the samba user. This is the password that will be used during authentication.
smbpasswd -a smbuserCreate Samba User
Next, we will create a new group for our secure samba share and add the new samba user.
groupadd smb_group
usermod -g smb_group smbuserThereafter, create yet another samba share which will be securely accessed. In our case, we have created another directory in the same path as the
mkdir -p /srv/tecmint/privateThen configure the file permissions for the samba share
chmod -R 770 /srv/tecmint/private
chcon -t samba_share_t /srv/tecmint/private
chown -R root:smb_group /srv/tecmint/privateOnce again, access the Samba configuration file.
$ sudo vim /etc/samba/smb.conf
Add these lines to define to secure samba share.
[Private]
path = /srv/tecmint/private
valid users = @smb_group
guest ok = no
writable = no
browsable = yesSave the changes and exit.
Finally, restart all the samba daemons as shown.
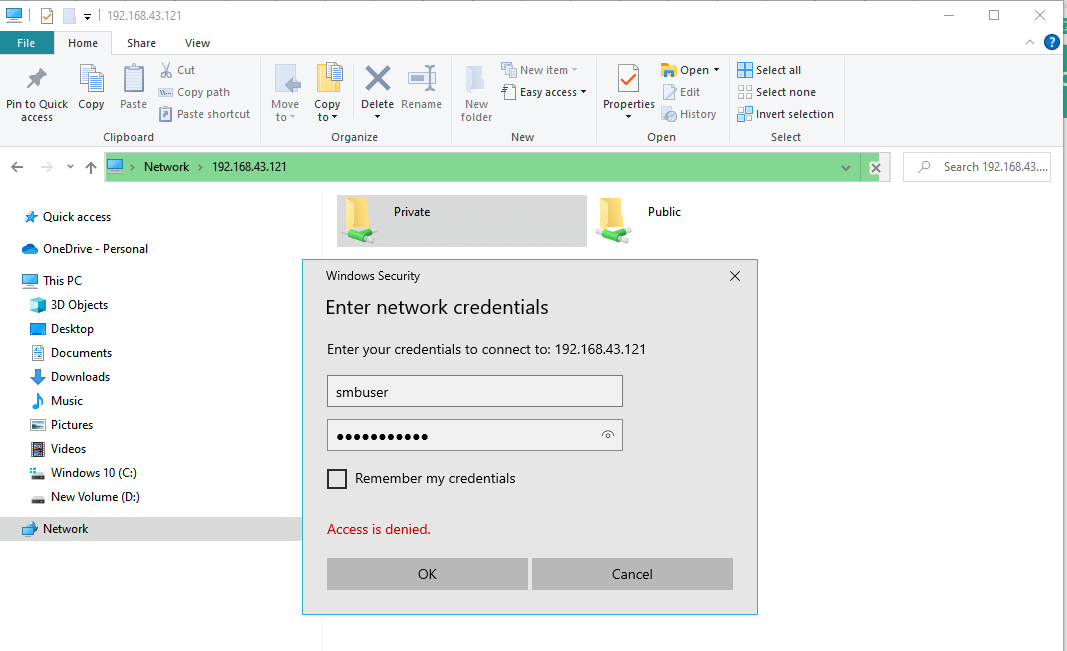
systemctl restart smb;systemctl restart nmbWhen you access your server this time around, you will notice an additional ‘Private‘ folder. To access the folder, you will be required to authenticate with the Samba user’s credentials. Provide the username and password of the user you created in the previous step and click ‘OK’.
Samba User Authentication
Step 5: Accessing Samba Share from Linux Client
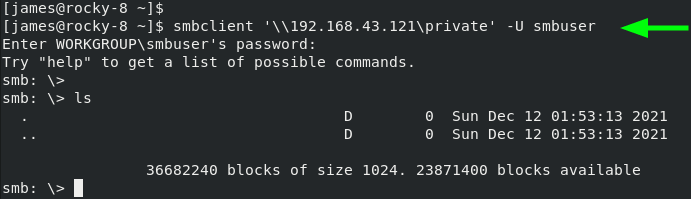
$ dnf install -y samba-clientThen use the smbclient command as follows
smbclient ‘\2.168.43.121\private’ -U smbuserAnd this concludes this guide on setting up Samba on RHEL, CentOS Stream, Rocky Linux, and AlmaLinux. Your feedback on this guide will be highly appreciated.
Some taken from https://www.tecmint.com/install-samba-rhel-rocky-linux-and-almalinux/